| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Watch this video animation of how DNA is packaged for a visual lesson in its structure.
Like ammonia, amines are weak bases due to the lone pair of electrons on their nitrogen atoms:

The basicity of an amine’s nitrogen atom plays an important role in much of the compound’s chemistry. Amine functional groups are found in a wide variety of compounds, including natural and synthetic dyes, polymers, vitamins, and medications such as penicillin and codeine. They are also found in many molecules essential to life, such as amino acids, hormones, neurotransmitters, and DNA.
Since ancient times, plants have been used for medicinal purposes. One class of substances, called alkaloids , found in many of these plants has been isolated and found to contain cyclic molecules with an amine functional group. These amines are bases. They can react with H 3 O + in a dilute acid to form an ammonium salt, and this property is used to extract them from the plant:
The name alkaloid means “like an alkali.” Thus, an alkaloid reacts with acid. The free compound can be recovered after extraction by reaction with a base:
The structures of many naturally occurring alkaloids have profound physiological and psychotropic effects in humans. Examples of these drugs include nicotine, morphine, codeine, and heroin. The plant produces these substances, collectively called secondary plant compounds, as chemical defenses against the numerous pests that attempt to feed on the plant:
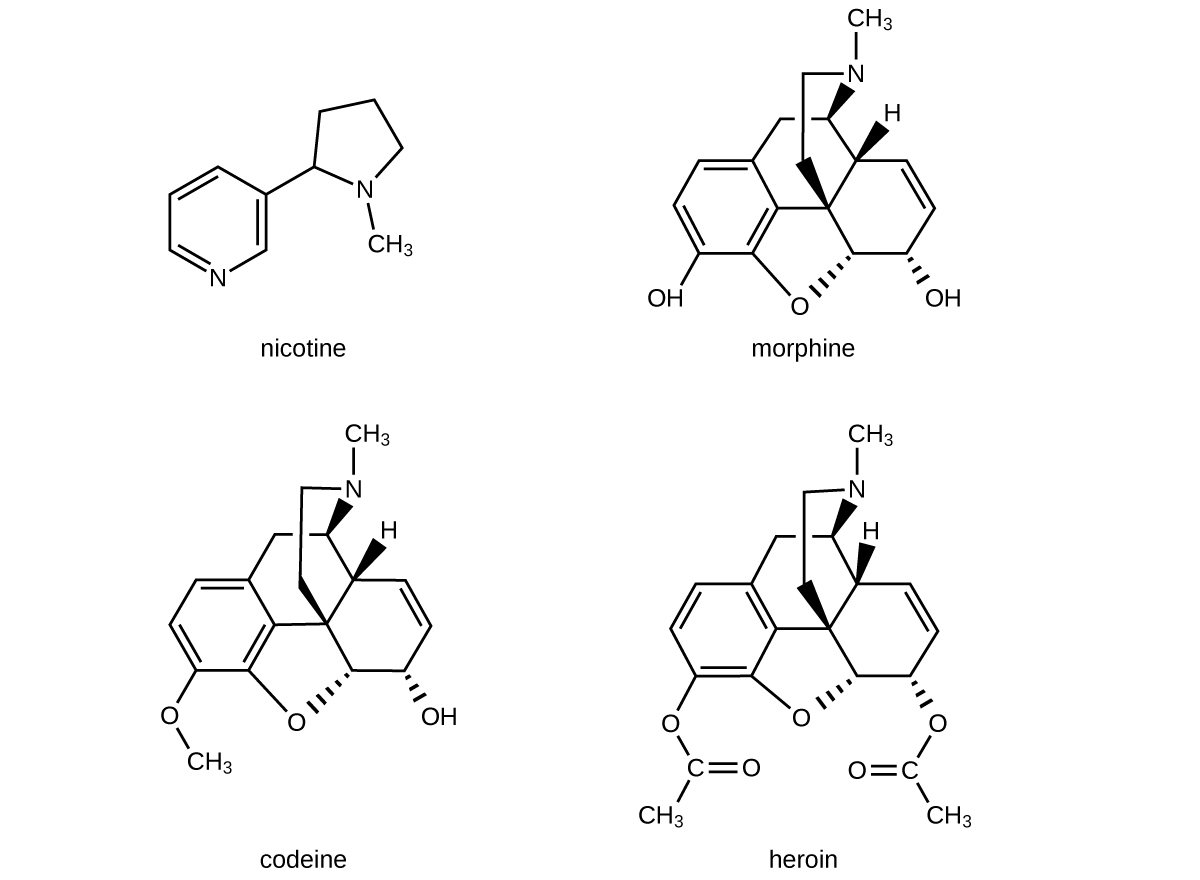
In these diagrams, as is common in representing structures of large organic compounds, carbon atoms in the rings and the hydrogen atoms bonded to them have been omitted for clarity. The solid wedges indicate bonds that extend out of the page. The dashed wedges indicate bonds that extend into the page. Notice that small changes to a part of the molecule change the properties of morphine, codeine, and heroin. Morphine, a strong narcotic used to relieve pain, contains two hydroxyl functional groups, located at the bottom of the molecule in this structural formula. Changing one of these hydroxyl groups to a methyl ether group forms codeine, a less potent drug used as a local anesthetic. If both hydroxyl groups are converted to esters of acetic acid, the powerfully addictive drug heroin results ( [link] ).

Amides are molecules that contain nitrogen atoms connected to the carbon atom of a carbonyl group. Like amines, various nomenclature rules may be used to name amides, but all include use of the class-specific suffix -amide :
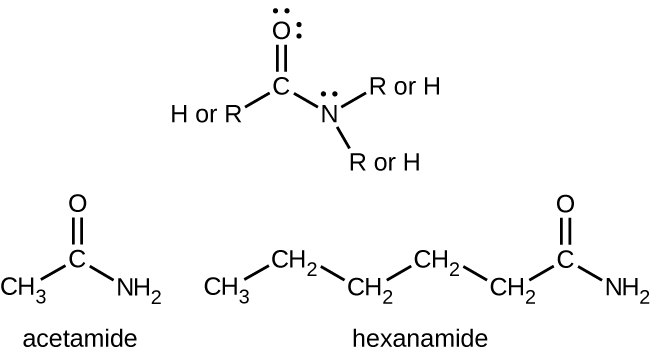
Amides can be produced when carboxylic acids react with amines or ammonia in a process called amidation. A water molecule is eliminated from the reaction, and the amide is formed from the remaining pieces of the carboxylic acid and the amine (note the similarity to formation of an ester from a carboxylic acid and an alcohol discussed in the previous section):

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?