| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
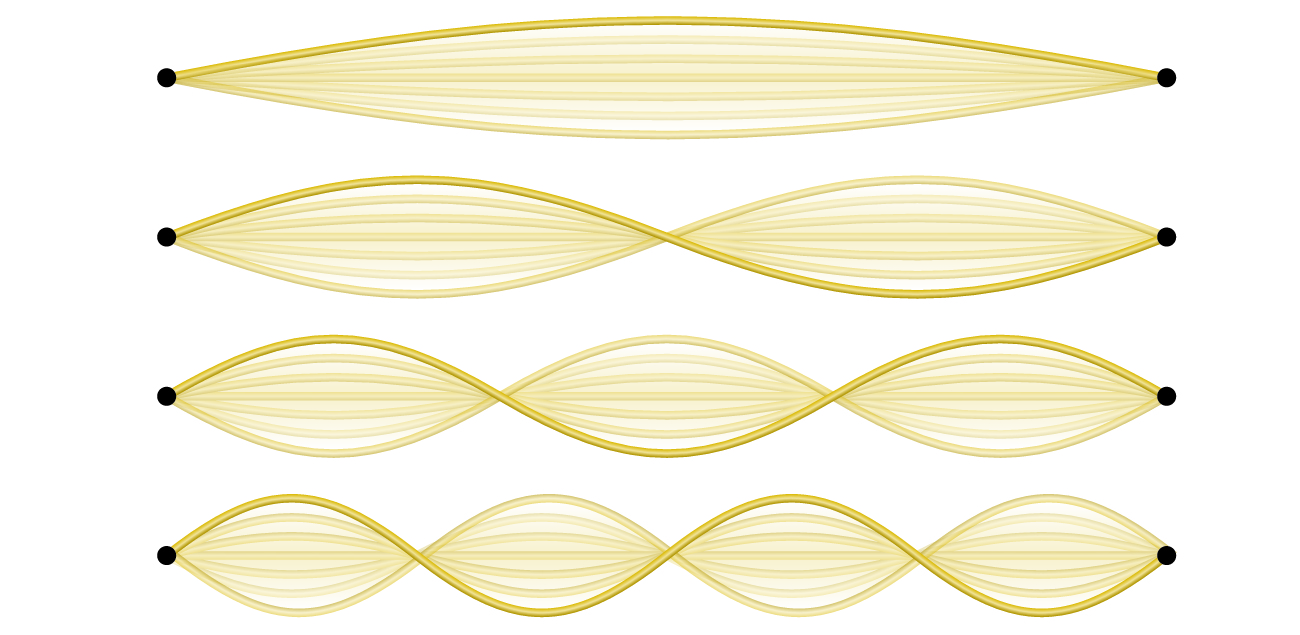
An example of two-dimensional standing waves is shown in [link] , which shows the vibrational patterns on a flat surface. Although the vibrational amplitudes cannot be seen like they could in the vibrating string, the nodes have been made visible by sprinkling the drum surface with a powder that collects on the areas of the surface that have minimal displacement. For one-dimensional standing waves, the nodes were points on the line, but for two-dimensional standing waves, the nodes are lines on the surface (for three-dimensional standing waves, the nodes are two-dimensional surfaces within the three-dimensional volume). Because of the circular symmetry of the drum surface, its boundary conditions (the drum surface being tightly constrained to the circumference of the drum) result in two types of nodes: radial nodes that sweep out all angles at constant radii and, thus, are seen as circles about the center, and angular nodes that sweep out all radii at constant angles and, thus, are seen as lines passing through the center. The upper left image in [link] shows two radial nodes, while the image in the lower right shows the vibrational pattern associated with three radial nodes and two angular nodes.

You can watch the formation of various radial nodes here as singer Imogen Heap projects her voice across a kettle drum.
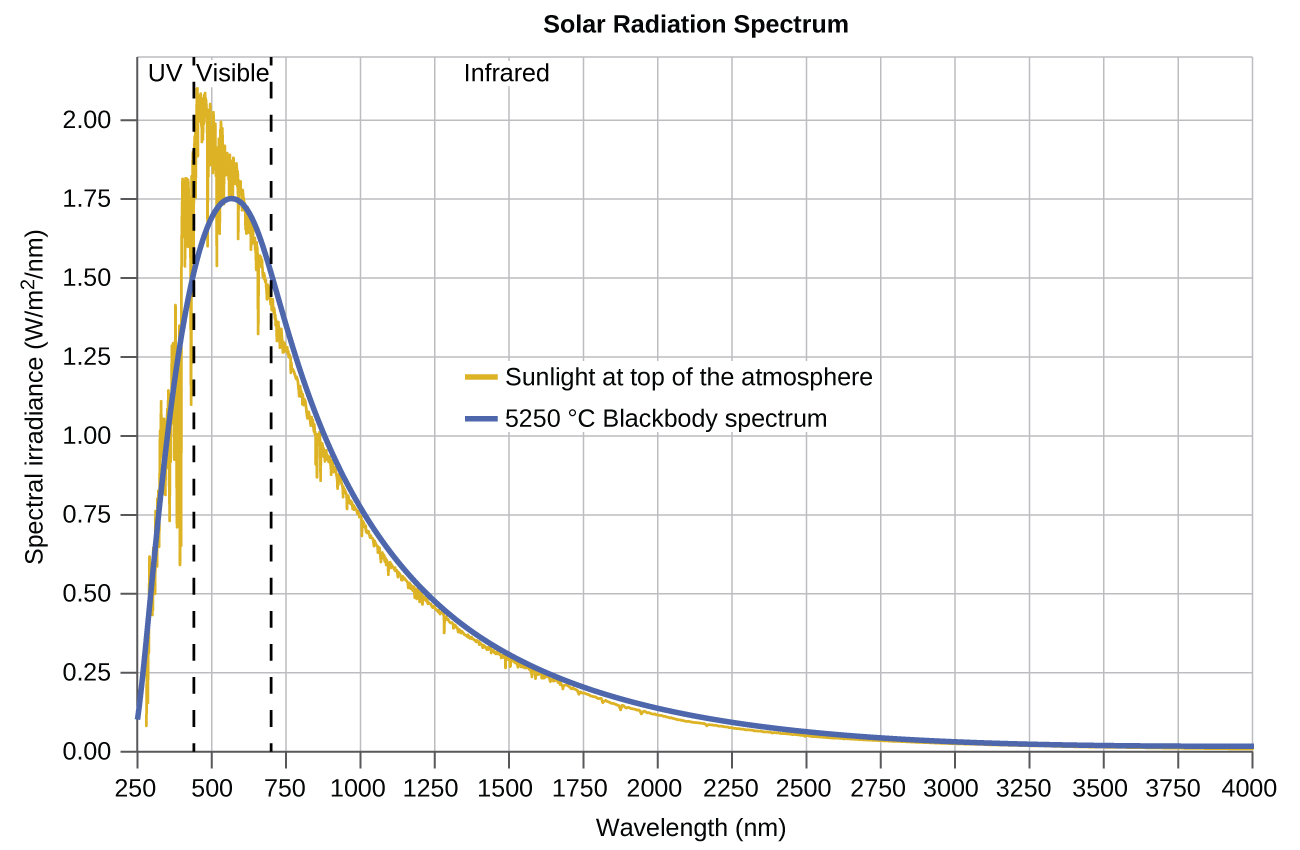
The last few decades of the nineteenth century witnessed intense research activity in commercializing newly discovered electric lighting. This required obtaining a better understanding of the distributions of light emitted from various sources being considered. Artificial lighting is usually designed to mimic natural sunlight within the limitations of the underlying technology. Such lighting consists of a range of broadly distributed frequencies that form a continuous spectrum . [link] shows the wavelength distribution for sunlight. The most intense radiation is in the visible region, with the intensity dropping off rapidly for shorter wavelength ultraviolet (UV) light, and more slowly for longer wavelength infrared (IR) light.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?