| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

[link] uses ray tracing to show how an image is formed when an object is held closer to a converging lens than its focal length. Rays coming from a common point on the object continue to diverge after passing through the lens, but all appear to originate from a point at the location of the image. The image is on the same side of the lens as the object and is farther away from the lens than the object. This image, like all case 2 images, cannot be projected and, hence, is called a virtual image . Light rays only appear to originate at a virtual image; they do not actually pass through that location in space. A screen placed at the location of a virtual image will receive only diffuse light from the object, not focused rays from the lens. Additionally, a screen placed on the opposite side of the lens will receive rays that are still diverging, and so no image will be projected on it. We can see the magnified image with our eyes, because the lens of the eye converges the rays into a real image projected on our retina. Finally, we note that a virtual image is upright and larger than the object, meaning that the magnification is positive and greater than 1.
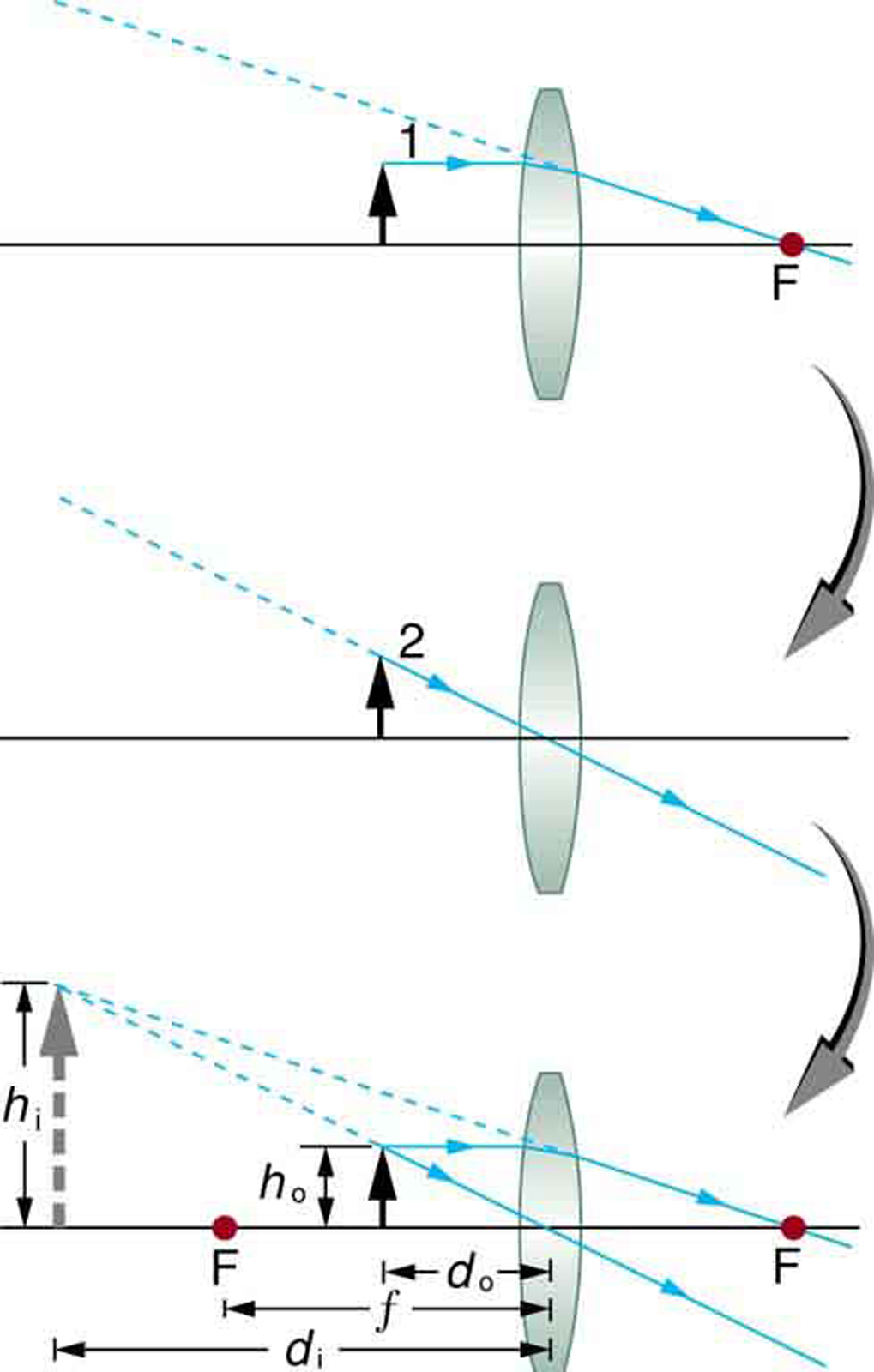
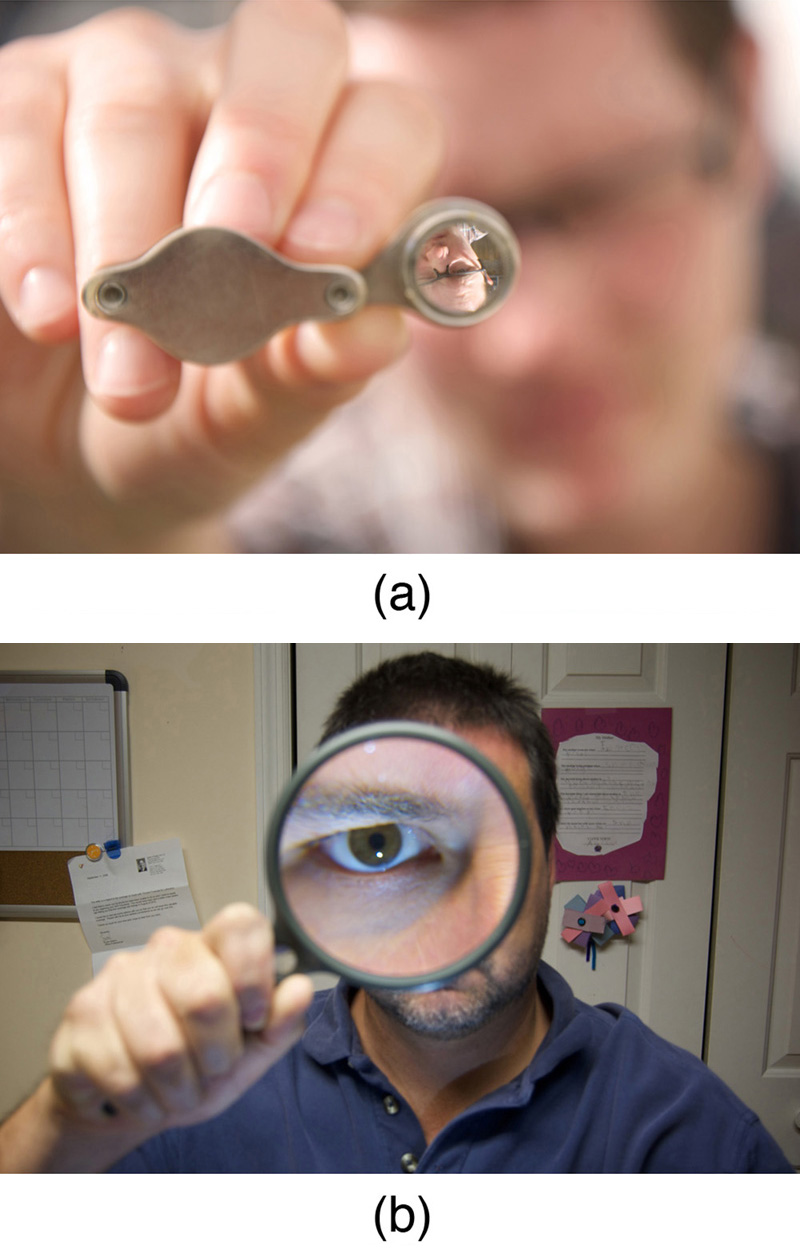
An image that is on the same side of the lens as the object and cannot be projected on a screen is called a virtual image.
Suppose the book page in [link] (a) is held 7.50 cm from a convex lens of focal length 10.0 cm, such as a typical magnifying glass might have. What magnification is produced?
Strategy and Concept
We are given that and , so we have a situation where the object is placed closer to the lens than its focal length. We therefore expect to get a case 2 virtual image with a positive magnification that is greater than 1. Ray tracing produces an image like that shown in [link] , but we will use the thin lens equations to get numerical solutions in this example.
Solution
To find the magnification , we try to use magnification equation, . We do not have a value for , so that we must first find the location of the image using lens equation. (The procedure is the same as followed in the preceding example, where and were known.) Rearranging the magnification equation to isolate gives

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?